Refraction Microtremor (ReMi) è una tecnica basata sulle onde di superficie di Rayleigh ed è stata sviluppata dal 2004 dal Dott. John Louie (et. al.).
Fintanto che le onde viaggiano all'interno di un mezzo dispersivo, possono essere registrate da un array lineare di geofoni da 4.5Hz verticali, permettendo di analizzare la lentezza e le frequenze delle onde registrate dall'array.
Considerando le proprietà penetrative delle varie frequenze, è possibile modellizzare un profilo 1D del sottosuolo stimando velocità e profondità degli strati e, a seconda della lunghezza massima dello stendimento utilizzato, si possono raggiungere profondità maggiori rispetto alla MASW, utilizzando lo stesso stendimento con qualche minuto di registrazione passiva.
Dataset acquisito con il DoReMi.
Sfruttando il rumore naturale generato dalle varie sorgenti, come il traffico, l'attività umana e/o le vibrazioni indotte da fenomeni naturali come il vento su strutture ed alberi, si può generare un sismogramma finale di alcuni minuti, dal quale si può calcolare lo spettro su cui fare il picking e poi la modellazione.
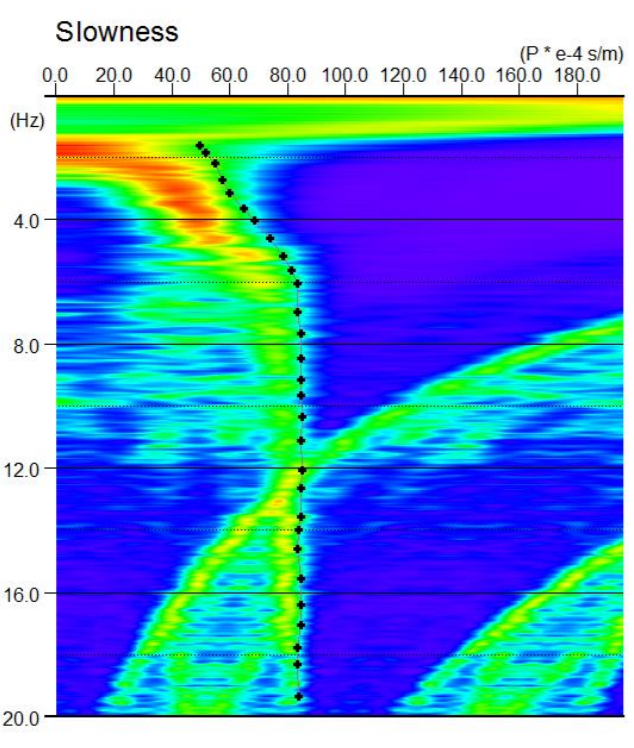 Picking della curva di dispersione calcolata con la tecnica ReMi.
Picking della curva di dispersione calcolata con la tecnica ReMi.